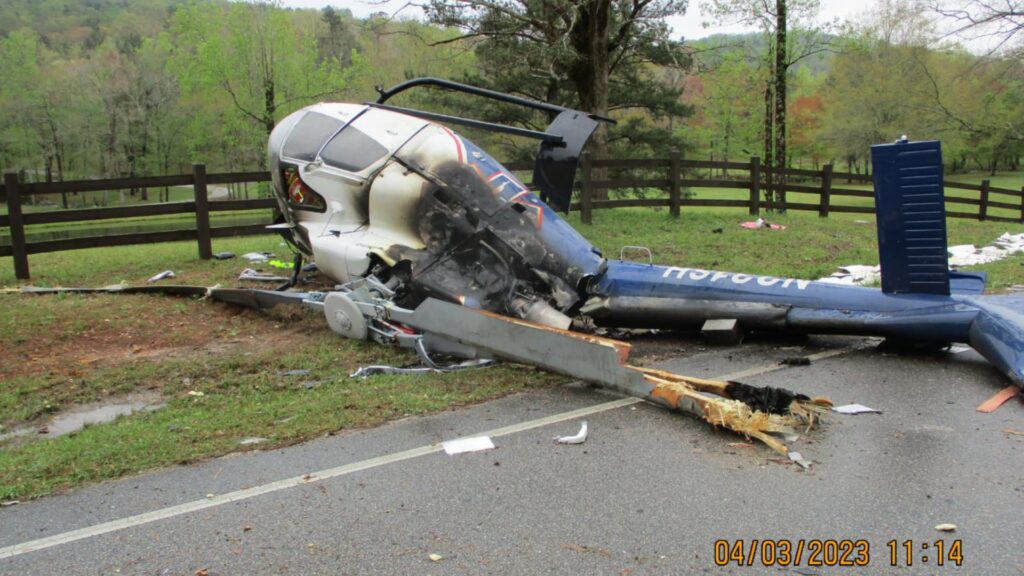
On the evening of April 2, 2023, what began as a routine medical mission ended in tragedy near Chelsea, Alabama. An Airbus EC130 T2 helicopter, operating under Part 135 as an air ambulance flight, crashed during a maneuver, claiming the lives of the 63-year-old pilot and a flight nurse, and leaving a flight paramedic seriously injured. The accident starkly reminds us of how crucial human factors and decision-making are in aviation—especially when lives depend on timely and safe operations.
A Routine Mission Turns Deadly
At approximately 5:23 p.m., witnesses along a rural road spotted the helicopter hovering low—just 3 to 4 feet above the ground—parallel to the roadway. The helicopter appeared stable initially, but soon climbed rapidly and turned toward the road. It passed above a vehicle, hovered momentarily, and then executed a 180-degree turn toward an open field.
What happened next was catastrophic. The aircraft suddenly pitched nose-down and crashed onto the road behind the witnesses. A dashcam from a nearby sheriff’s deputy captured the chilling moment: the helicopter reemerged from behind trees in a steep nose-down attitude before impacting the ground. It skidded about 20 feet before coming to a rest in the grass, with the wreckage consumed by post-crash fire.

No Mechanical Failures—But a Critical Delay in Control
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) investigation found no evidence of mechanical failure. The helicopter’s airframe, engine, and control systems appeared free of any pre-impact malfunctions that would have prevented normal operation. Video from an onboard recorder showed that until the final hover, the flight was uneventful.
During that last hover, however, the situation deteriorated rapidly. The helicopter’s altitude increased from about 50 feet to 110 feet above ground level, but the nose pitched up over 20 degrees and rolled right about the same amount—far beyond normal parameters. Despite visible trees ahead, the pilot made no significant control inputs to correct this excessive pitch and roll until the helicopter had already begun to nose over uncontrollably. His delayed response—moving the cyclic left and aft—was too late. The aircraft crashed nearly perpendicular to the road.
A Highly Experienced Pilot, but Low Time in Type
The pilot, who tragically perished in the accident, was highly experienced overall, with 8,965 total flight hours and 8,495 hours as pilot-in-command. However, he had only 18 hours in the EC130 T2—a relatively low amount of experience in this specific aircraft type. He held a commercial certificate with a helicopter instrument rating and a current second-class medical certificate.

A Hidden Threat: Medication Impairment
Perhaps the most sobering aspect of this tragedy lies in the toxicology findings. The pilot’s blood and tissue tested positive for multiple sedating substances: cetirizine (an antihistamine), cyclobenzaprine (a muscle relaxant), and diphenhydramine (another sedating antihistamine). Each of these drugs alone can impair cognitive and motor functions, and when combined, they pose a significant risk to vigilance, concentration, reaction time, and psychomotor performance.
The NTSB concluded that the pilot’s use of these central nervous system depressants likely contributed to his delayed and inadequate control inputs during the critical moments of the flight.
Key Safety Takeaways
This accident illustrates multiple important lessons for pilots, especially those in high-stakes operations like air medical transport:
- Know your medications. Even over-the-counter drugs like diphenhydramine (commonly found in cold medications) and cetirizine (used for allergies) can impair performance. Combining these with prescription muscle relaxants magnifies the risk.
- Respect transition time when flying new aircraft types. Although the pilot was highly experienced overall, his limited time in the EC130 T2 could have affected his ability to instinctively recognize and correct an unusual attitude in a timely manner.
- The importance of self-assessment. Pilots must continuously evaluate their fitness for flight—not only in terms of health, fatigue, and recency, but also potential effects of any medications they’ve taken.
- Crew resource management (CRM) is critical. While this mishap was driven by the pilot’s control inputs, CRM strategies and protocols may provide additional safety nets in similar scenarios, especially during dynamic and high-workload operations like air medical missions.

Final Thoughts
This Chelsea, Alabama, helicopter accident underscores the unforgiving nature of aviation—especially when human performance is compromised. While mechanical reliability is essential, the ultimate safeguard rests in the hands and judgment of the crew. As sobering as this event is, it offers vital lessons that can help prevent future tragedies in the air medical and broader rotorcraft communities.











One Comment
Sad, sad. Effects of self medication are a growing problem. Sometimes it is difficult to know when to say no.